NoSQL
Introduction
A NoSQL database provides a mechanism for storage and retrieval of data that is modeled in means other than the tabular relations used in relational databases.
The data structures used by NoSQL databases (e.g. key–value pair, wide column, graph, or document) are different from those used by default in relational databases, making some operations faster in NoSQL. The particular suitability of a given NoSQL database depends on the problem it must solve. Sometimes the data structures used by NoSQL databases are also viewed as "more flexible" than relational database tables.
In the sense of the CAP theorem NoSQL stores compromise consistency in favor of availability, partition tolerance, and speed.
Types of NoSQL databases
NoSQL databases (aka "not only SQL") are non tabular, and store data differently than relational tables. NoSQL databases come in a variety of types based on their data model.
The main types of NoSQL databases are:
They provide flexible schemas and scale easily with large amounts of data and high user loads.
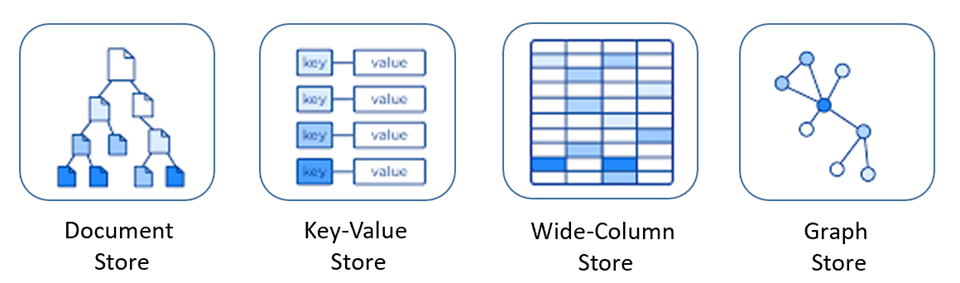
Each type of NoSQL database is designed with a specific customer situation in mind, and there should be technical reasons for how each kind of database would be organized.
When to use a NoSQL database?
NoSQL database technology is usually adopted for one or more of the following reasons:
- NoSQL databases allow developers to be in control of the structure of the data, they are a good fit with modern rapid Agile development practices based on sprints, quick iterations, and frequent code pushes.
- NoSQL databases are often better suited to storing and modeling structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data in one database.
- NoSQL databases are often based on a scale-out strategy, which makes scaling to large data volumes much cheaper than when using the scale-up approach the SQL databases take. Scale-out architectures also provide benefits such as being able to upgrade a database or change its structure with zero downtime.
- NoSQL databases were created during the cloud era and have adapted quickly to the automation that is part of the cloud. Deploying databases at scale in a way that supports microservices is often easier with NoSQL databases.